ZK KYC VS CRYPTOBIOMETRICS – A detailed comparison

We all know that Web3 offers innovative ways for users to interact and transact directly – without the need for middlemen, but at the same time, this freedom brings its own set of problems. Suppose you want to keep your stuff private while at the same time, you need to prove you’re who you say you are, and you don’t trust the party that you need to prove yourself to because they are known to sell personal data. Yet, you do understand that security is just as important to protect against cyber threats, which are becoming increasingly common as blockchain adoption grows.
Similarly, transparency, another core principle of Web3, builds trust by making transactions visible and verifiable on the blockchain. However, this visibility can sometimes conflict with the need for privacy, especially when personal information is involved.
Unfortunately the pseudonymous nature of Web3 platforms has led to a rise in various scams. In the first quarter of 2024, $739.7M worth of cryptocurrency was stolen, with a significant portion of these losses due to exploits that took advantage of the pseudonymity provided by blockchain.
Governance attacks, Flash loan attacks, Sybil attacks, and other forms of manipulation within decentralized finance (DeFi), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and airdrop events highlight the need for identity verification mechanisms that can restrain such abuses while respecting user privacy.
The question that arises here is how do we create trust in systems that are easy targets for impersonation, bots, and fraud?
Proof-of-personhood is gaining traction as a go-to solution, helping drive Web3 into the mainstream for things like digital governance, public funding, universal basic income (UBIs), and civic causes.
On the other hand, tools like "Sign in With Google," Robinhood’s KYC, captchas, and Apple’s FaceID have made things like web accounts, government IDs, and biometrics a regular part of life. People are paying attention to how well these methods can block fake accounts and bot attacks. But are they the actual solutions?
You see, blockchain lets you be pseudonymous, which is great if you value privacy. But this anonymity also makes it easy for scammers to pull tricks. Think about it: in DAOs or during airdrops, people have found ways to game the system using multiple identities.
That’s a big deal, and it shows why we need some kind of verification to prove that a person is who they claim to be. But here’s the catch— How much of your info should you give up to prove who you are? Too much, and you lose privacy; too little, and you open the door to fraud.
The Web3 industry is stepping up to tackle this problem with new ways to prove who you are without giving away all your details. In this article, we’ll dive into two of these technologies: Zero Knowledge Know Your Customer (ZK KYC) and Cryptobiometrics.
Both technologies are starting to gain traction, so we felt it is time to sit down and compare how ZK KYC and Cryptobiometrics handle the tricky balance between privacy, security, and transparency. Each has its way of keeping your data safe while making sure you’re legit. So, where do they shine, where they fall short, and which might be the best fit for different situations.
Let’s start by first exploring What KYC in Web3 means and why it's such an issue:
In Web3, verifying who someone is—without giving away too much personal information—is a tricky challenge. Traditionally, KYC has been a way for banks and financial institutions to verify the identities of their customers. They do it by collecting personal information like your ID documents, address, and sometimes even more detailed data like your employment history or income.
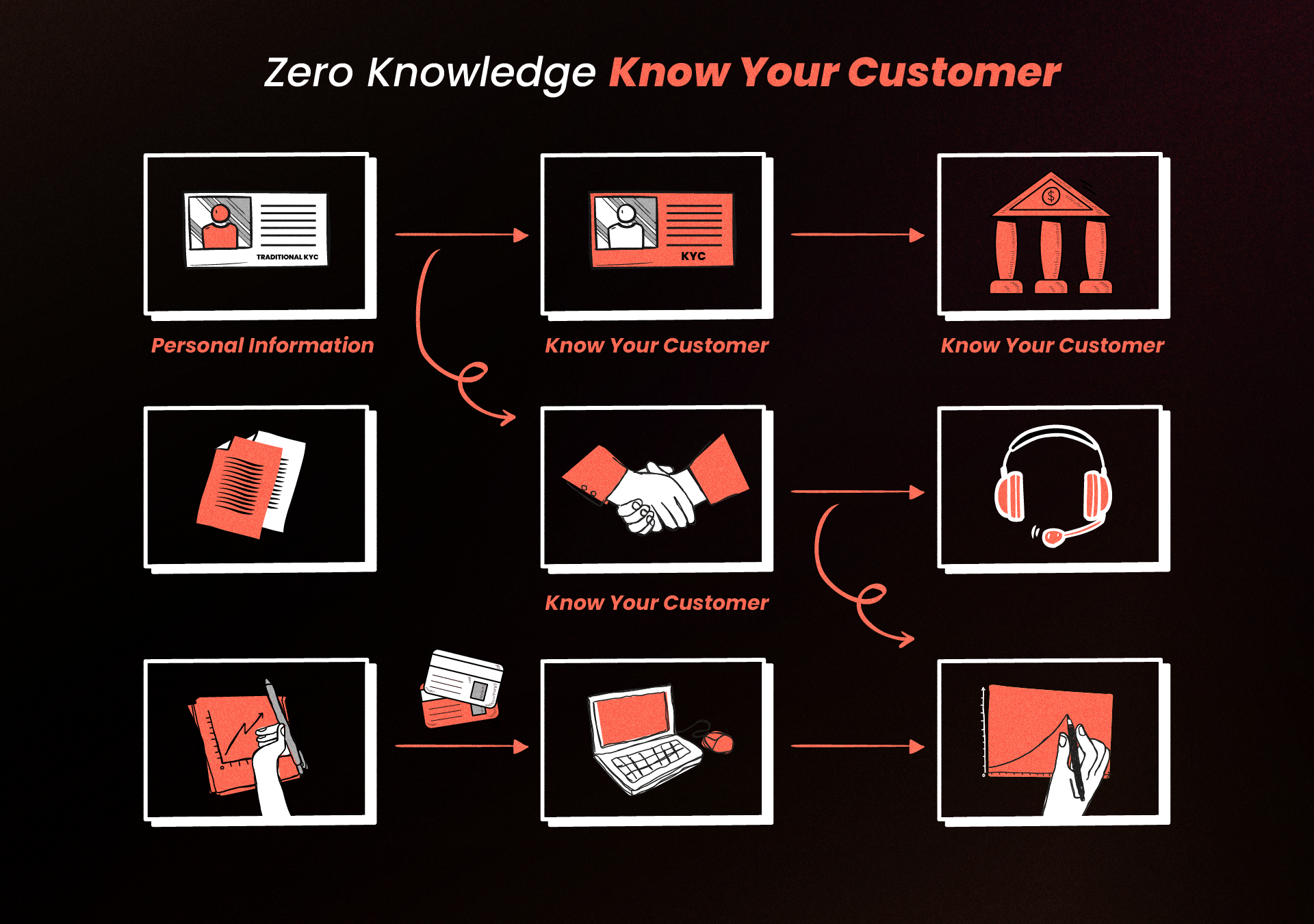
But Web3 is different. It’s built on the idea of decentralization, where control and power are distributed across many users rather than centralized in a single entity. Asking people to hand over their personal information goes against this principle, making many Web3 users uncomfortable. For example, when Shapeshift, a popular crypto platform, introduced KYC requirements, it saw a massive drop in its user base—like, just about 95%—because people didn’t want to give up their privacy.
So, how does Web3 handle this? This is where the concept of ZK KYC and cryptobiometrics comes into play.
Let’s first explore both technologies one by one.
What is Zero Knowledge (ZK) KYC?
Imagine you’re at a club, but instead of showing your ID to prove you’re old enough to enter, you just show a card that says, “This person is over 18.” The bouncer doesn’t need to know your name, your address, or anything else about you—just that you’re allowed in. That’s the basic idea behind Zero Knowledge (ZK) KYC.
Zero Knowledge KYC is a method of verifying identity without revealing any sensitive personal information. It allows someone to prove they are who they say they are without sharing details like their name, address, or date of birth. This is made possible through the use of cryptography and blockchain technology. With ZK KYC, you can essentially say, “I’m trustworthy,” without having to hand over a bunch of personal data once more.
Why Does This Matter?
In the traditional world, KYC processes are standard—banks ask for a lot of information to ensure you are who you claim to be. This includes your government ID, proof of address, and even sometimes your employment details. But in Web3, where the core value is decentralization and privacy, this approach feels invasive. It’s like walking into a party where everyone values their privacy and being asked to announce your full name and share your personal history.
With ZK KYC, the benefits are clear:
- Privacy: You can prove your identity without giving away any personal details. This reduces the risk of data breaches because there’s no sensitive data stored that hackers could steal.
- Security: Since there’s no need to store personal data, the risks of cyber-attacks are significantly lowered, making Web3 safer for everyone involved.
- Ease of Use: Traditional KYC processes often require you to submit multiple documents, which can be time-consuming. ZK KYC simplifies and speeds up this process, allowing for quicker verification.
How Does It Work?
Think of Zero Knowledge KYC as a way of proving something without showing the evidence. Let’s say you’re in a secret club, and the only requirement to join is that you’ve solved a very difficult puzzle. Instead of showing everyone how you solved it (which could reveal your secrets), you show them a special certificate that proves you did it. They trust the certificate because it’s been verified by someone they all agree is reliable.
In the context of Web3, this “certificate” is a cryptographic proof that confirms your identity without revealing the underlying data. For example, after verifying your identity with a third party, you receive a cryptographic seal. This seal can then be used to prove you’re a real person when accessing services, without ever showing your original documents or personal information.
Understanding Cryptobiometrics
Cryptobiometrics, on the other hand, uses your biometrics (facial for now) data (along with liveness detection) as your key to access a decentralized network. It allows you to verify your identity without ever asking for personal details.
Unlike traditional methods or even Zero Knowledge (ZK) KYC, Cryptobiometrics doesn’t ask for your name, address, or any other personally identifiable information (PII), it only proves that a person behind an account is a unique living human being, not a bot or multi-account holder.
It’s all about your biometric data—like a 3D scan of your face—which gets encrypted and used to confirm your identity.
Think of it as a digital key that only you can use. The system checks if you’re legit, but it never needs to know who you are beyond that.
In Humanode Biomapper all you need to prove your uniqueness is an EVM wallet that is tied to a unique biometric token with a signature that you can get during Biomapper flow.
For any smart contract on Humanode Chain, checking someone’s uniqueness is as simple as:
bool isUnique = ICheckUniqueness(BIOMAPPER_CONTRACT_ADDRESS).isUnique(
addressToCheck
);
Why Does This Matter?
We’re all used to using our faces to unlock phones or log into apps. But most of these systems are run by big companies that store your data, raising concerns about privacy and security. Who’s really in control of your information? What about the info being exploited by governments?
Cryptobiometrics flips the script by keeping your data encrypted, decentralized, and private even from Humanode. You prove who you are without giving up control of your personal information. It’s like getting the benefits of biometric security without the downsides of centralization.
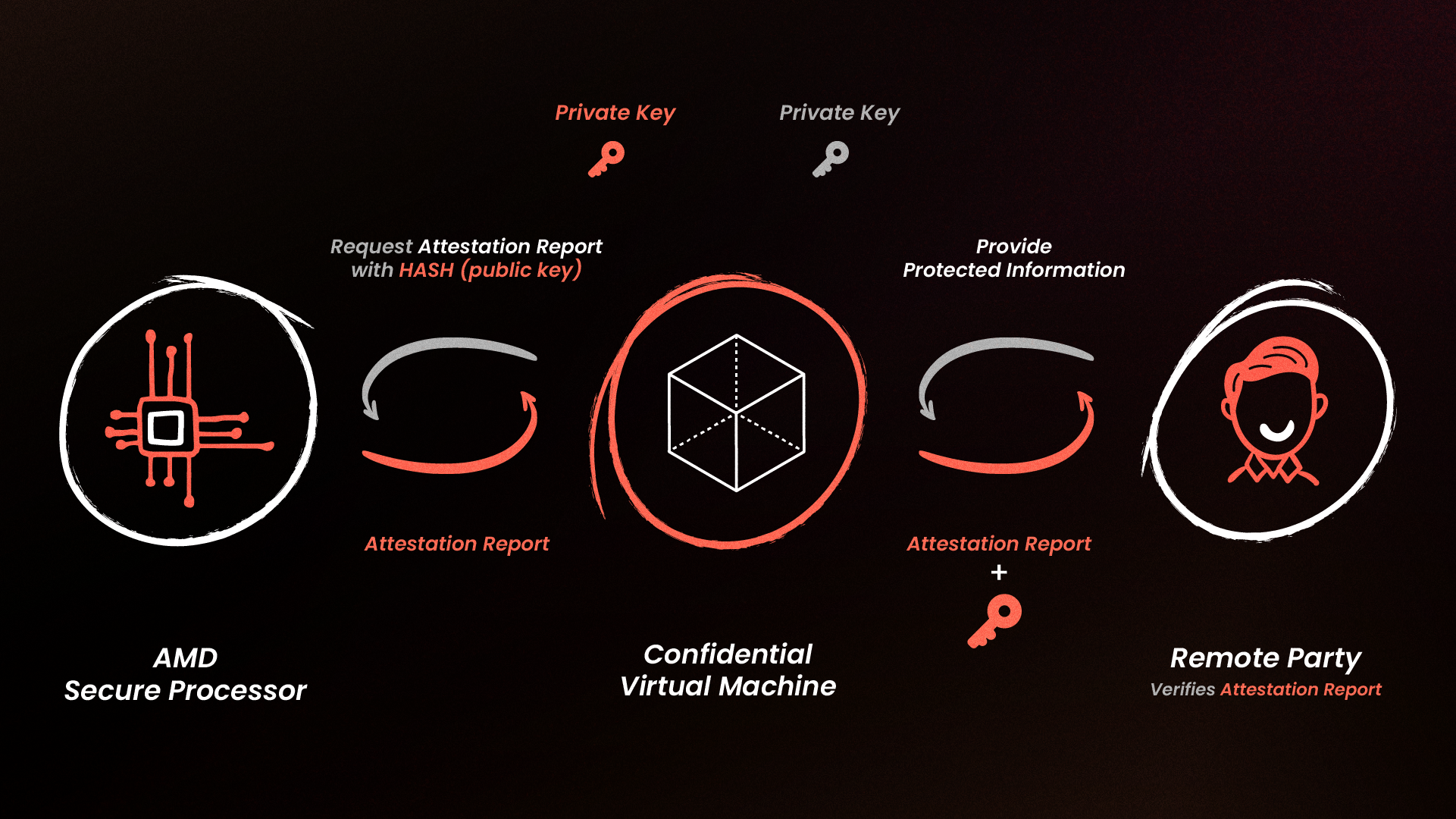
How It Works?
- Data Collection: You start by doing a quick 10-15 second live video scan of your face. The system creates an anonymized 3D template and checks that you’re a real, live person—not a photo, mask, or deep fake.
- Encryption and Transmission: Your 3D face template and liveness data get encrypted right on your device. Then, it’s sent securely to Confidential Virtual Machines (VMs), where it’s protected from unauthorized access, even from the people running the servers.
- Data Verification: Your encrypted data is compared with what’s already stored to verify your identity. This all happens in a secure, encrypted space, so your actual facial data stays private. The liveness data is deleted immediately after verification, ensuring only live users get access.
- Data Storage: Once verified, your encrypted face template is stored securely, and a Biotoken—a random string—is created. This Biotoken is tied to your blockchain account but can’t be used by anyone else, keeping your data safe.
Here’s why cryptobiometrics tech is secure:
- Isn’t actually KYC: Unlike traditional KYC or even ZK KYC which is masked KYC itself, cryptobiometrics is different. It just proves that a unique human being is tied to the account or service, and that the account does not belog to a bot or a multi-account holder.
- No Personal Info Needed: One of the perks of Cryptobiometrics is that you don’t need to provide any personal information like your ID documents or birthdate. The encrypted 3D mapping data derived from your face is enough to verify that you match, or do not match the data in the system. In fact, there’s no risk of your details getting leaked because personal identifiable private data is never collected.
- Liveness Detection: The system checks that you’re alive during the face scan, preventing fake identities from getting through. This feature is key to keeping the network secure. Humanode uses Facetec’s highly accurate liveness detection, with a chance of error of only 1/1250,000. This high level of accuracy ensures that deep fakes, photos, video streams, and other fake identities are effectively blocked from accessing the network.
- Big Deal for Decentralization: Decentralized networks like Humanode aim to give everyone access without relying on central authorities. Cryptobiometrics fits perfectly with this idea by offering a secure, private way to verify identities without giving up your info.
- 1 Person = 1 Vote = 1 Node: In DeFi apps and DAOs, ensuring that each participant is unique is crucial. Without this, individuals could create multiple identities (a Sybil attack) to gain more influence or control. Cryptobiometrics helps to prevent this. You can read more about the use cases here.
- Fairness and Security: By linking each person to a single identity, Cryptobiometrics helps DeFi platforms and DAOs operate on an equal basis. This reduces the risk of individuals manipulating the system, whether in voting or financial transactions.
Comparing ZK KYC and Cryptobiometrics
Now that we’ve laid out what ZK KYC and Cryptobiometrics are all about, let’s put them side by side and see how they stack up when it comes to privacy and security in Web3. Below is a comparison in key areas.
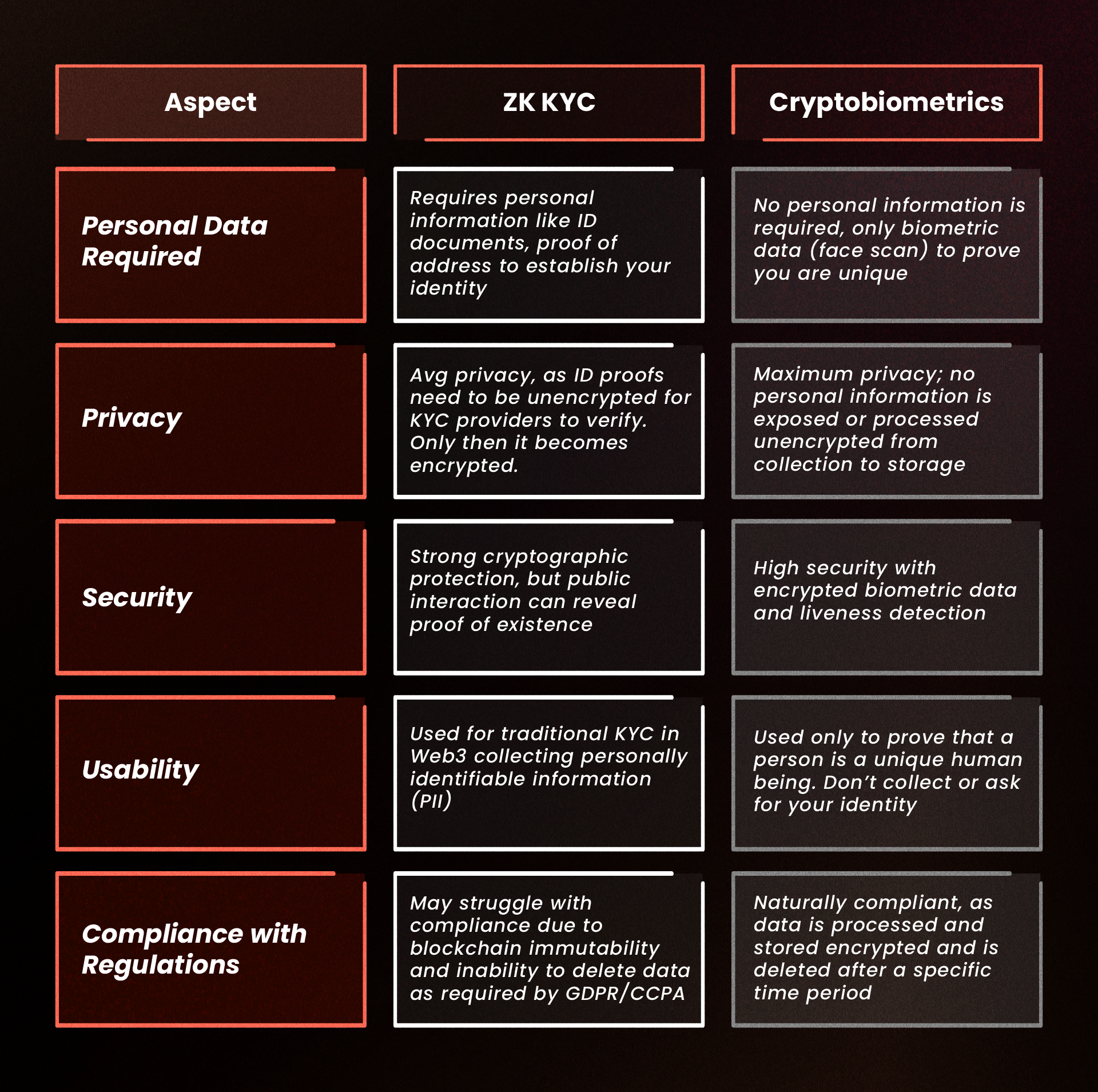
- Privacy
- ZK KYC:
Strengths: ZK KYC is designed to keep your personal data private by generating cryptographic proofs without revealing any underlying information. It’s particularly good at minimizing the amount of data exposed during identity verification processes.
Weaknesses: The main issue with ZK KYC is that even though the content of the proof remains private, the existence of the proof can become public when a wallet interacts with a public smart contract. This can partially negate the privacy benefits of ZK technology.
- Cryptobiometrics:
Strengths: Cryptobiometrics doesn’t require any personal information. It uses only your biometric data (such as a face scan) to verify your identity, ensuring that no sensitive personal information is ever exposed or stored on the blockchain.
Weaknesses: The challenge lies in ensuring the security and accuracy of the biometric data, which is handled by sophisticated encryption and liveness detection technology.
- Security
- ZK KYC:
Strengths: ZK KYC offers strong cryptographic protection, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access sensitive information.
Weaknesses: Unfortunately, ZK proofs are linked to wallet addresses through signatures. If these proofs become publicly discoverable when interacting with public smart contracts, the security benefits can be compromised. Moreover, the need for continuous dynamic updates to ZK proofs adds complexity to maintaining security over time.
- Cryptobiometrics:
Strengths: Cryptobiometrics provides high security through the use of encryption, and it ensures that only verified, living individuals can access the network. Humanode’s liveness detection, for instance, has a high success rate, making it highly effective against deep fakes and other spoofing attempts.
Weaknesses: The reliance on hardware and secure transmission processes, such as those provided by AMD SEV-SNP, is crucial. While these technologies are advanced, any breach in these areas could pose risks.
- Usability
- ZK KYC:
Strengths: Simplifies traditional KYC processes by allowing users to verify their identities without directly sharing their personal information with third parties.
Weaknesses: The need to generate new proofs for each interaction and the potential exposure of proof existence in public blockchains can complicate the user experience.
- Cryptobiometrics:
Strengths: Offers a straightforward user experience where the face scan is the primary requirement. No need for additional personal information or repeated verification steps.
Weaknesses: The initial setup of biometric data and ensuring a compatible device might require more effort from the user.
- Compliance with Privacy Regulations
- ZK KYC:
Challenges: Storing personal information on a blockchain, even in encrypted form, can lead to non-compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA. Since blockchain data is immutable, deleting personal data upon request—required by these regulations—is not feasible.
- Cryptobiometrics:
Advantages: Since no personal information is stored or shared, Cryptobiometrics is naturally aligned with privacy regulations. The system’s design prevents the storage of any data that could be traced back to an individual, making it more compliant with privacy laws.
Summing Up
When it comes to Web3 privacy, Cryptobiometrics stands out. It doesn’t ask for your PII documents, uses encryption and liveness detection to securely prove that the person behind an account is a unique living human being, and aligns with the decentralized nature of Web3.
ZK KYC, on the other hand, is KYC that encrypts your identity information documents. Although it offers strong privacy, it faces challenges, especially during initial document collection and keeping proofs private during blockchain interactions.
For those Web3 projects, those who want to perform KYC can use ZK KYC instead of traditional KYC but will still be required to comply with data regulations.
For those looking for privacy, security, and simplicity in decentralized networks, Cryptobiometrics provides a solid option. It supports the "1 person = 1 vote = 1 node" principle, ensuring fairness in DeFi applications and DAOs. Other than that, cryptobiometrics can be used for airdrops, Whitelisting campaigns, and other such events where projects want to ensure that Sybils do not spoil their rewards distribution while at the same time preserving privacy.
A prime example of cryptobiometrics at work is Humanode’s BotBasher for Discord. The basic idea behind BotBasher for Discord is that there is a unique human being behind each Discord account. To date, BotBasher is being utilized by more than 400 Discord servers and has successfully verified 500K+ users.
Apart from BotBasher, Humanode’s Biomapper is another successful product that uses cryptobiometric technology to map one EVM address to one unique human. Biomapper can be utilized by Dapps and Web3 projects to enable Sybil-resistant Login and Sign Ups on their app.
Here's how you can use Biomapper to enable Sybil resistance in your Dapps.
- https://github.com/humanode-network/biomapper-sdk/tree/master/usage
- https://github.com/humanode-network/biomapper-sdk/tree/master/examples
Here’s how the claim function for a sybil-resistant airdrop contract could look like:
function claim() public {
require(!isAlreadyClaimed[msg.sender], "User has already claimed");
require(BIOMAPPER.isUnique(msg.sender), "User is not unique");
ERC20_TOKEN.safeTransferFrom(TOKEN_VAULT, msg.sender, AMOUNT_PER_USER);
isAlreadyClaimed[msg.sender] = true;
emit Claimed(msg.sender);
}
To learn more about cryptobiometrics and how you can use it, check out the Humanode Whitepaper, explore Confidential Virtual Machines (CVM) for data security, and visit Humanode’s Biomapper Repos to see the technology in action.

